The social media movement: The creation of online and offline communities using social media in the Black Lives Matter Movement.
Jessica Petrides
THE SOCIAL MEDIA MOVEMENT
Abstract
This paper explores the use of social media platform Twitter and its ability to create strong communities online, which are then taken offline to enact change. I will examine what determines a virtual community and the factors that contribute to creating a strong virtual community. Building on this, I will explore how virtual communities have to capacity to transcends to that of one which also exists offline. This paper will use the Black Lives Matter movement as an example to demonstrate the way in which the online activist movement also created an offline movement by organising protests, rallies and boycotts.
Keywords: Black Lives Matter, social media, online communities, Twitter.
THE SOCIAL MEDIA MOVEMENT
Social networking sites (SNS’s) have the ability to connect a wide range of demographics, from all over the world, to form online communities. These virtual communities can be used to spread awareness, create support systems, facilitate relationships and generate strong-ties between users (Porter, 2015). These virtual communities also have the capacity to transfer to offline communities. An example of this is Black Lives Matter, an originally online community which has become an offline movement. The movement, which utilises the social media platform Twitter, fights to spread awareness against racial disparity in America, and was created following unfortunate events of mistreatment to African Americans. Originally starting as a hashtag (#blacklivesmatter), the movement transformed into on ground protests, boycotts and rallies right around America. By delving deeper into both the online and offline communities that Black Lives Matter has created, I will be exploring how SNS’s have the capability to go further than just virtual interaction, and its ability to spread awareness and form communities that gather face-to-face in the world to achieve a shared goal.
Social media communities and the Black Lives Matter movement
Porter (2015) describes virtual communities as passion-centric, where the focal point of the communication by individuals is a shared interest and the interaction of this is supported by technology. To build a strong virtual community there are a set of factors which create its foundations. These factors include a fulfilment of needs, shared emotional connection between members and a sense of belonging (Hersberger, Murray, & Rioux, 2007). Because of these foundations, the assumption for a well maintained community should include content and support which reaches its member’s expectations, be engaging and act in solidarity. As Forman, Kern, and Gil-Egui (2012) discuss, the fulfilment of needs, shared emotional connection and sense of belonging, are all factors which can be achieved in both virtual and face-to-face communities. This provides a transition from virtual community to face-to-face, and vice versa, to be that of a smooth one. Virtual communities forming on social media websites can be said to be split into two groups, computer supported social networks (CSSNs) and the other, a network-based virtual community (Porter, 2015). CSSNs cover users who only communicate over computers and have the potential to have strong, moderate or weak ties. The second, network-based virtual communities, covers those individuals who are geographically dispersed where members seek social benefits (Porter, 2015). The creation of these online communities can be performed through gaming, chat rooms and social media. With the ease of access to social media, it can be utilised as a space to gather, communicate and discuss issues. This can be seen on Twitter, which now amasses over 330 million users worldwide (Statista, 2018). The creation of online communities assisted in creating a large and ongoing civil movement in the United States of America. The Black Lives Matter movement began in 2013, as a response to George Zimmerman’s acquittal of the shooting and killing of unarmed, 17 year old, African American, Trayvon Martin. Created by Alicia Garza, Patrisse Cullors and Opal Tometi, three African American women who were united together in their stance to form a revolutionary peace movement, the term Black Lives Matter was created. The purpose of their movement was to, and to this day still is to, affirm African Americans humanity, contributions to society and resilience in the face of deadly oppression, as they wish to live in a world where black lives are no longer targeted for demise (“Herstory,” 2013). The movement is strong and powerful and truly took off in 2014, when protests commenced in Ferguson, Missouri, following the shooting and killing of Michael Brown, who was once again an unarmed, African American, teenager. Brown’s death by a white police officer gained a large amount of traction on Twitter, with the Black Lives Matter hashtag being tweeted about on an average of 58,747 times per day for three weeks after Michael Brown’s death (Anderson & Hitlin, 2016). The large amount of media coverage and response to this incident brought to light topics of national debate including race, rights and gun control. From these unfortunate events, and many others since (“Timeline: The Black Lives Matter movement,” 2018), the Black Lives Matter virtual community was born, and was used as a platform and tool to organise on-ground events for communities to engage in this social activism in person.
How Black Lives Matter created an online community
Black Lives Matter, which originally began as a hashtag on Facebook (#Blacklivesmatter), transcended into an extremely popular and widespread Twitter movement. It created a large community of users and from the movement entered a recognisable community, with its own agenda and identity, to end racial disparity and police brutality (Freelon, McIlwain, & Clark, 2016). Twitter emerged as a platform where users shared stories, found common ground in their concern of the events occurring and together were fighting for reform (De Choudhury, Jhaver, Sugar, & Weber, 2016). Millions of users expressed their concerns over brutality, and a recognisable community with its own agenda and identity formed (Freelon et al., 2016). This growing community utilised multiple hashtags, as shown in Table 1 in the appendix. With over 21 million tweets regarding the Ferguson riots, and over 9 million regarding the killing of Michael Brown. Millions of tweets including the names of other victims of police brutality were also posted. Members of this community were fighting give a voice to those who could no longer speak for themselves. Amongst the millions of tweets displayed in appendix one, De Choudhury et al. (2016) discovered that users with high participation in the movement rarely expressed high levels of negativity or anger in their posts. They were determined to fight for change, as a calm collective. They were firm in their stance to organise action and were socially connecting, supporting, coping and engaging with each other as a community (De Choudhury et al., 2016). The online community grew so rapidly in size, that these users had the capacity to spread news of any brutality and issues regarding the movement faster than mainstream media (Miners, 2014). Adding to this, Patterson (2016) found that the community associated with Black Lives Matter was larger than any communities that were associated with mainstream media outlets. This formed a powerful community that had the ability to be well-informed and knowledgeable and was able to control the speed of information dispersed. As Freelon et al. (2016) discusses, supportive communities consistently attract more attention than those that are unaligned or opposed, and the Black Lives Matter movement who involved users rallying together so their voices could be heard and their desire for change further discussed, is a prime example of this. Twitter support from celebrities including Lebron James, Kim Kardashian West and Lady Gaga among many more, expanded the movements reach even further (James, 2016; Kardashian West, 2016; Gaga, 2016). With celebrities having a reach of millions on Twitter, this type of traction on the issue assisted in the movements capacity to those outside of the community of the issues at hand.
How Black Lives Matter created an offline community.
From reaching millions to create a virtual community on Twitter, the Black Lives Matter movement also adapted to on-ground communities right around America. Using Twitter as the main platform, it was able to facilitate the organisation of Black Lives Matter protests, boycotts and rallies. The organisation of these demonstrations were not just completed by the founders of the movement, but were done by many individuals and other organisations who shared the same goals. From July 2014 to March 2018, over 2300 protests or other demonstrations were held in support of this movement . Some protests attracted thousands and lasted for days, the biggest, and most covered by the media being the Ferguson protests which attracted a great amount of worldwide media attention. Community members who were on-ground at the protests, continued to update members of the community who were unable to make the Ferguson protests due to geographical location (Freelon et al., 2016). DeRay McKesson was one of these community members who live-tweeted his experience at the protests. This total amount of retweets and mentions of the brutality that was displayed at the protests amassed to 1 million (Freelon et al., 2016). With people from around the world seeing what this community was capable of arranging, the protests not only become widespread throughout the United States, they also became international and continued to attract thousands, with solidarity marches held in Manchester, London, Birmingham and Bristol (Pidd, 2016). On-ground support of the movement was also demonstrated by celebrities who had originally expressed their support of the campaign via Twitter. Celebrity husband and wife duo John Legend and Chrissy Tiegen hired several food trucks to serve free food to those protesting the movement in New York, Jay Z and Beyonce hosted a charity ball where they raised $1.5 million to donate to social justice groups including Black Lives Matter, four NBA players delivered a speech at the opening of the 2016 ESPY (Excellence in Sports Performance Yearly) Awards where they brought to light their strong support of the Black Lives Matter movement and actor Jesse Williams produced a documentary titled ‘Stay Woke: The Black Lives Matter Movement’ (Price, 2016). This transition to what once began as a hashtag, to millions worth of donations, a documentary and people demanding action on-ground, is a true testament to what a Twitter movement has the capability to do.
Conclusion
As shown above in the Black Lives Matter movement, strong virtual communities have the ability to become offline communities. Virtual communities with strong foundations and a clear purpose as discussed by have similar characteristics to traditional communities, and therefore can be both online and offline. Twitter gave the Black Lives Matter movement a global audience and the employment of this social media form gave way for Twitter users to also become a part of on-ground activism rather than just online activism. The sheer magnitude of protests, boycotts, rallies and media attention the movement received is a testament to this. Although it is impossible to measure if the movement would have been as influential without the Twitter movement, I believe it would not have gained the vast amount of traction and support that is has, and still does.
Appendix:
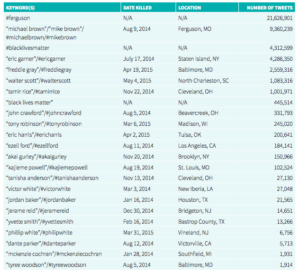
Table 1: Retrieved from “Beyond the Hashtags: #Ferguson, #Blacklivesmatter, and the Online Struggles for Offline Justice,” by D. Freelon, C. D. Mcllwain, and M. D. Clark, 2016.
References:
Anderson, M., & Hitlin, P. (2016). The hashtag #BlackLivesMatter emerges social activism on Twitter. Social Media Conversations About Race. Retrieved from http://www.pewinternet.org/2016/08/15/the-hashtag-blacklivesmatter-emerges-social-activism-on-twitter/#
At least 2,356 Black Lives Matter protests and other demonstrations have been held in the past 1,353 days. (2018). Retrieved from https://elephrame.com/textbook/BLM
De Choudhury, M., Jhaver, S., Sugar, B., & Weber, I. (2016). Social Media Participation in an Activist Movement for Racial Equality. Proceedings of the … International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media. International AAAI Conference on Weblogs and Social Media, 2016, 92-101.
Forman, A. E., Kern, R., & Gil-Egui, G. (2012). Death and mourning as sources of community participation in online social networks: R.I.P. pages in Facebook. 2012. doi:10.5210/fm.v0i0.3935
Freelon, D., McIlwain, C. D., & Clark, M. D. (2016). Beyond the Hashtags: #Ferguson, #Blacklivesmatter, and the Online Struggle for Offline Justice.
Gaga, Lady. (2016, August 7). Paul O’neal…[Tweet]. Retrieved from https://twitter.com/ladygaga/status/762381066682273792?lang=en
Hersberger, J. A., Murray, A. L., & Rioux, K. S. (2007). Examining information exchange and virtual communities: an emergent framework. Online Information Review, 31(2), 135-147. doi:10.1108/14684520710747194
Herstory. (2013). Black Lives Matter. Retrieved from https://blacklivesmatter.com/about/herstory/
James, L. (2016, July 7). This article says it all…[Tweet]. Retrieved from https://twitter.com/kingjames/status/751234227836841989
Kardashian West, K. (2016, July 8). BLACK LIVES MATTER [Tweet]. Retrieved from https://twitter.com/kimkardashian/status/751430737304252416?lang=en
Miners, Z. (2014). Analysis of Ferguson tweets shows Twitter’s quick grip on the news. Retrieved from PCWorld website: https://www.pcworld.com/article/2540140/analysis-of-tweets-around-ferguson-shows-twitters-quick-grip-on-the-news.html
Patterson, B. E. (2016). Black Lives Matter is Killing it on Twitter. Retrieved from Mother Jones website: https://www.motherjones.com/politics/2016/03/study-shows-how-black-lives-matter-controls-police-narrative/
Pidd, H. (2016). Thousands attend Black Lives Matter solidarity march in Manchester. Retrieved from The Guardian website: https://www.theguardian.com/uk-news/2016/jul/11/black-lives-matter-solidarity-march-protest-manchester
Porter, C. E. (2015). Virtual communities and social networks. In L. Cantoni & J. A. Danowski (Eds.), Communication and technology (Vol. 5, pp. 161-179): Walter de Gruyter GmbH & Co KG.
Price, L. (2016). How Celebrities have Supported Black Lives Matter. Retrieved from People Celebrity website: http://people.com/celebrity/how-celebrities-have-supported-black-lives-matter/#the-weeknd
Statista. (2018). Number of monthly active Twitter users worldwide from 1st quarter 2010 to 4th quarter 2017 (in millions). Retrieved from: https://www.statista.com/statistics/282087/number-of-monthly-active-twitter-users/
Timeline: The Black Lives Matter movement. (2018). Retrieved from ABC News website: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2016-07-14/black-lives-matter-timeline/7585856
This work by Jessica Petrides is licensed under a: Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License
