Social media stands today as an essential tool for activism because it provides a platform to encourage social transformations and a place of expression for public opinion. Emma Watson successfully developed her Instagram platform to support environmental sustainability with the combination of her famous reputation and online reach whilst also fostering ecosystem-wide climate change protection efforts. Watson proves through her work that virtual communities within social networking sites like Instagram, can motivate users to participate in environmental activities beyond the digital space. The research analyzes how Watson implements Instagram advocacy through an evaluation of her environmental activities within global conservation efforts and social media’s capacity to initiate worldwide change initiatives.
Environmental sustainability advocacy through celebrity endorsements has flourished extensively on Instagram as one of the prominent social media platforms. Emma Watson shares critical environmental information with international users both as an actress and activist about environmental problems and possible solutions to drive the audience toward unified action for sustainability support. Watson uses her popular influence to create shared responsibility among her followers who then participate through sustainable environmental conservation initiatives throughout the globe. The network Watson has built serves both to promote her herself as an actress and to enable collective activism in support of environmental movements that match her personal brand. This advocacy falls under the identity and online advocacy stream. Watson uses her digital presence to educate her audience by sharing environment related posts and stories relevant to influencers or other activists/organisations approaching similar ideas and empower the public to find active participation within environmental activism. The analysis presented in this paper involves Emma Watson’s Instagram-based activism through detailed examples which demonstrate how social media connects to global movements. When Watson interacts with her followers in the virtual environment, she generates spaces where environmental conservation ideas grow to produce genuine ecological transformation. This paper examines how Watson utilizes the concepts of social networking sites together with virtual community dynamics to use Instagram’s worldwide audience for promoting environmental causes and raising awareness. The examples discussed within the paper prove that social media can effectively function as a useful tool which advances social and environmental activism.
Emma Watson wins recognition as a British actress since her portrayal of Hermione Granger in Harry Potter films while additionally leading influential actions for gender equality and environmental sustainability. Through her role as a UN Women Goodwill Ambassador she uses her influential position to defend multiple social issues specifically concentrating on environmental protection work (Shende, 2024.) Through Instagram, Watson uses her substantial audience to emphasize the importance of environmental stability while posting content and stories about sustainable matters, climate change and the necessity of group effort. Watson shares environmental knowledge through Instagram, combined with informative posts about inspiring quotes that let users find methods to help environmental conservation. For example, as seen on Watsons Instagram profile, content such as Figure 1. Is a posted quote by Higgins about how instead of the law being served for people and their property, for the public to imagine a law that puts people and the planets wellbeing first. The quote encourages us to develop legal frameworks which place the health of people and planet at their center because environmental well-being directly shapes human success and justice.

Figure 1. Climate change quote- Emma Watsons Instagram profile.
Through her platform on Instagram, Watson regularly presents content created by other environmental activists and organizations as well as supporters who promote similar causes. The combination of voice amplification for aligned individuals produces a stronger sustainable message for public awareness (Long, 2025.) Through the practice of sharing environmental organization posts and the work of activists, Watson builds an online community which unites her followers to fight for environmental causes together. For instance, Figure 2. demonstrates a woman activist named Dominique Palmer, who has spoken together with Watson at the New York times Hub advocating for taking action in keeping the planet a better place for the future of humanity. (Shado-Mag, 2025.) On Instagram Emma Watson uses posts about comparable activists to support their work while spreading awareness about members of the same community who focus on social and environmental issues. Her Instagram platform serves to unite her followers through the promotion of environmental sustainability activists who she supports in addition to helping their causes, gain visibility. Such posts establish a virtual environment that helps people from different backgrounds connect to share concepts in an online community. Instagram enables collaborative action through group efforts who work together towards unified causes.

Figure 2- Climate justice activist speech- Emma Watsons Instagram profile.
Through the power of social media this technique of using comparable activists and deep quoting on her platform, establishes a digital area for environmental conservation concepts to unite multiple users thus proving social media’s ability to demonstrate collective action. Watson posts content with the goal of mobilizing people into environmental activities which includes waste reduction and sustainable business promotion (Ramazzina, 2016.) Through her platform Watson promotes worldwide environmental efforts and joint actions that expand her impact into major movements.
The text ‘A Networked Self: Identity, Community, and Culture on Social Network Sites’ (Papacharissi, 2010) analyses the perception that social networking platforms like Facebook and MySpace function as virtual communities. The platforms operate under principles that replicate virtual community settings, such as Instagram in this day in age. Researchers within the article agree about the necessity to study “community” definitions more precisely. As it is still argued whether an online community is just the illusion of one or if it truly can replicate a sense of one. In this statement it is agreeable that an online community can be replicated and suitable for many individuals who cannot appear face to face for community work or discussions. It helps accessibility within individuals who may not be able to physically attend and for activities to be carried out through virtual settings. Social networking websites built during modern times including Facebook and MySpace as mentioned in the article, operate using the vintage concept of online community development. Users can establish actual friendships, along with getting help from community members through social networking platforms which duplicate traditional community functions. The capability of online platforms to mimic traditional communities remains subject to expert scholarly disagreement because some researchers find they create solid social networks, yet others claim the term ‘community’ may be misused in this context (Papacharissi, 2010.) The web provides its users a distinctive environment in which global communications enable them to build worldwide support networks and connections beyond geographical constraints. Such accessibility together with interconnectedness leads to an extensive network of people who cooperate for common aims and interests.
The concept of “community” has been debated for nearly 200 years as mentioned in the chapter of ‘What constitutes community’, (Papacharissi, 2010) it is evolving alongside changes in society, technology, and political conditions. Some scholars argue that traditional, close-knit communities were weakened by urbanization and industrialization, leading to more disconnected, impersonal social ties. However, others believe the rise of online communities, like virtual ones on social media, is a response to a growing desire for stronger, more meaningful connections. While some see online communities as legitimate, others question whether they can truly replicate the emotional bonds and physical presence of traditional communities. For example, online communities must engage in collective action, share information regularly, and create strong emotional connections among members to be considered genuine communities. Social media platforms, by fostering these elements, help build virtual spaces where people can connect, share, and act together even without physical proximity.
Howard Rheingold examines virtual communities as meaningful connection areas through his book Virtual Communities: Homesteading on the Electronic Frontier (Papacharissi, 2010). The digital environment enables people to unite from diverse locations to share thoughts while performing collective tasks and building group identity during goal attainment. Social networking sites (SNSs) have progressed into multiple online communities that focus on various objectives, one of which is environmental sustainability. Through Watons Instagram platform, Emma demonstrates how proper use of online communities allows people to support environmental sustainability goals. Through her position as an actress and activist Watson connects with SNS capabilities to build an internet community focused on environmental education and activism. Workers who follow Watson through her posts receive awareness about essential environmental matters while she asks them to participate collaboratively by backing sustainable practices, waste reduction and advocating for political alterations. Rheingold’s discussion about virtual communities matches precisely with Watson’s endeavors. Watson’s Instagram functions as a digital platform that brings together sustainability-focused individuals into one digital community similar to MySpace and Facebook’s social spaces. Watson uses her posts to spotlight environmental activists’ work, so she builds a cohesive network which enables people to collaborate and take collective action. Watson uses shared environmental responsibility as well as collective actions to demonstrate that virtual communities have the power to trigger genuine world change. Through her Instagram advocacy she proves that virtual online platforms form communities which take the place of conventional physical groups for transborder activism causes. Online environmental activism demonstrates that social network platforms successfully unite numerous people into collective action toward environmental protection. Within Watsons Instagram platform her posts such as shown below in Figure 3.
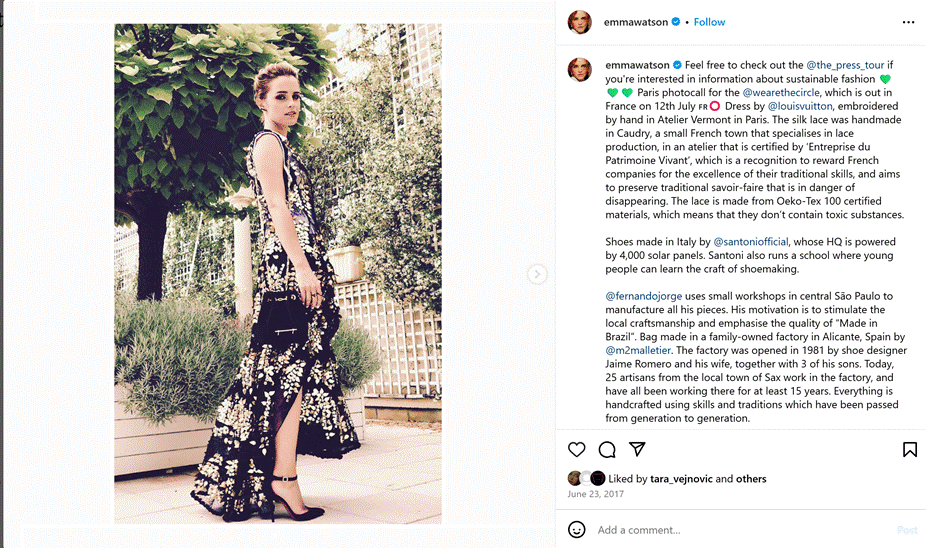
Figure 3. Sustainable fashion post on Instagram, proving Watsons dedication to promoting and living sustainably.
On Instagram Watson discusses environmental sustainability while also showing her commitment by selecting sustainable fashion options. The actress advocates sustainable brands and encourages eco-friendly strategies along with participating in ethical fashion initiatives through her promotions. The specific commitment to sustainable choices provides concrete evidence for people who want to pursue environmentally aware actions. Rheingolds theory (Papacharissi 2010) is proven through Watsons work as she finds new ways to bring sustainability enthusiasts together on Instagram. Through promoting activists and sustainable brands, Watson creates an online community which enables her followers to join forces for environmental action.
The Fridays For Future movement; FFF (Shim, 2024) established itself as a major voice within public climate change communication and mobilization strategies. Environmental campaigns like FFF now thrive on Instagram through the platform that allows activists to develop and spread their individual climate change stories. Through Instagram, Emma Watson conveys similar messaging that centers on climate emergency education and behavioral mobilization efforts. Watson effectively employs her Instagram platform to create a digital network dedicated to sustainability through both personal accounts of her climate activism and MAPA spotlight features. The FFF organisation use ways of personalizing climate change that rely on homemade content such as art and memes to link local issues with worldwide climate problems. Activists achieve personalization of their climate change message through tying global effects of change, directly to specific local areas. As explored in the article; Personalising climate change—how activists from Fridays for Future visualise climate action on Instagram, internet users from Mexico and Colombia participate in FFF’s live video exchanges to communicate their personal environmental experiences while showing their protest locations and neighborhood environmental problems. Through individualized local narratives, activists make environmental stakeholders aware of climate change effects across communities even though global effects affect everyone but have specific regional differences in their impact. Through this storytelling, it forms a shared activism from various locations to join forces toward achieving climate justice. An example of an FFF post is present on Watsons Instagram platform as shown in Figure 4.

Figure 4. Fridays for Future campaign post
The content Watson shares effectively makes people aware of local environmental conflicts and reinforces the understanding that climate change affects us on multiple levels from global to local scales. The visual storytelling style alongside personal communication on Instagram makes followers both participate and think about their neighborhood environmental problems while taking part in shared sustainability activism (Huang 2023.) Instagram transforms into an instrumental platform that creates an international climate activism community which implements true-world transformations through collective stories and activism. Instagram users can leverage the given tools such as @mentions to increase their personalized activism efforts as Challa (2024) mentions. FFF members connect their personal narratives through tagging activists and organizations which expands their collective reach and relays the message. FFF create collages and other content that cause others to participate in climate discussions which builds both local and global climate movement solidarity. Digital space becomes stronger because this method allows various voices to combine interests for a shared objective.
Through Emma Watsons platform she achieves both increased awareness and the formation of a shared virtual community whose members collaborate for global conservation. This position matches the main argument presented in this paper demonstrating that social networking through online advocacy effectively connects people into a powerful virtual community that produces societal evolution. Social media enables Watson to bridge geographical boundaries by connecting people internationally to address urgent environmental problems. Social networking platforms such as Instagram showcase their ability to unite collective powers through Greta Thunberg’s usage which promotes Fridays for Future along with her platform thus demonstrating how digital networks contribute to establishing worldwide sustainability movements. Through Watsons Instagram account, she provides education that enables her audience to empower themselves through concrete actions which demonstrate the power of online communities against global challenges. She promotes other activists along with environmental organisations to build an interconnected community focused on environmental conservation thus showing that social media can drive substantial worldwide change.
References:
Dominique Palmer. (2025). ShadoMag. https://shado-mag.com/author/dominique-palmer/
Hasfi, N., & Rahardjo, T. (2019). The Disabled People Virtual Communities in Social Media from The Perspective of Public Sphere Theory. Jurnal Komunikasi Ikatan Sarjana Komunikasi Indonesia, 4(2), 65–76. https://doi.org/10.25008/jkiski.v4i2.327
Long, F., Ye, Z., & Luo, L. (2025). Joint collective action increases support for social change and mitigates intergroup polarisation: A registered report. Journal of Experimental Social Psychology, 118, 104732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jesp.2025.104732
Papacharissi, Z. (2010). A networked self. In Routledge eBooks. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203876527
Ramazzina, Y. (2016). Emma Watson: Changing the World One (Sustainable) Dress at a Time. elephant journal . https://www.elephantjournal.com/2016/05/emma-watson-changing-the-world-one-sustainable-dress-at-a-time/
Shim, D. (2024). Personalising climate change—how activists from Fridays for Future visualise climate action on Instagram. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03556-7
Super human race. (2024). A celebrity for climate change. Super human race do good things.https://www.mysuperhumanrace.com/story-details/MTQwNw==/a-celebrity-for-climate-change
4 Instagram screenshots
Figure 1- Watson, E. [@emmawatson]. ( 2021, December 21st posted). The rules of our world are laws and they can be changed. [Instagram post]. https://www.instagram.com/p/CXwDEOkryRI/?hl=en&img_index=1
Figure 2- Watson, E. [@emmawatson]. (2021, November 9th posted). Dominique Palmer is a climate justice activist and organiser in Fridays for Future International. [Instagram post]. https://www.instagram.com/p/CWDfVp3sA03/?hl=en
Figure 3- Watson, E. [@emmawatson]. (2017, June 23rd posted). Feel free to check out the @the_press_tour if you’re interested in information about sustainable fashion. [Instagram post]. https://www.instagram.com/p/BVqFbtMBgPa/?hl=en&img_index=1
Figure 4. Watson, E. [@emmawatson]. (2021, October 29th posted) Fridays for Future. [Instagram post]. https://www.instagram.com/p/CVlTVZZvb8n/?hl=en&img_index=1

Hi Shannon Kate, You’re right to ask; it is incredibly difficult to police these issues today. Predatory behaviour isn’t exclusive…